Lyon Animal Intensive Care Unit
- Letter to the Editor
- Open Access
- Published:
Animal ICU… Why not also use the existing veterinary ICUs?
- Céline Pouzot-Nevoret2,3,
- Vanessa Louzier2,
- Isabelle Goy-Thollot2,3,
- Anthony Barthélemy2,3,
- Stéphane Junot2,
- Jeanne-Marie Bonnet-Garin2 &
- Bernard Allaouchiche2,4
Annals of Intensive Care volume 9, Article number:93 (2019) Cite this article
-
1621 Accesses
-
5 Altmetric
-
Metrics details
We have read with interest the article published recently in the journal by Guillon et al. "Preclinical septic shock research: why we need an animal ICU" [1]. The authors review the limitations of current animal models in septic shock especially the lack of heterogeneity and comorbidities, and argue the need to develop animal intensive care unit (ICU) to better reflect the reality of human management.
We agree with the authors that rodents poorly reflect human conditions, and that financial and ethical issues are the main limitations to perform experiments in larger species. However, another way to explore therapies in sepsis, which was not mentioned by the authors, is the use of clinical models (in particular canine and feline) treated in existing veterinary ICUs. Our young research unit "Agressions Pulmonaires et Circulatoires dans le Sepsis" (APCSe) is composed of veterinary and medical physicians, and we have a platform for ovine and porcine experiments where we are able to reproduce ICU conditions for large-animal preclinical models [2, 3]. We also have access to a veterinary ICU at the veterinary school in Lyon (VetAgro Sup) where dogs and cats are treated for severe sepsis. For example, we previously explored hemodiafiltration [4] or hemostatic disorders in dogs suffering from multiple organ failure due to leptospirosis [5]. This approach provides solutions to the limitations highlighted by the authors: different weights, different ages and not only two conditions (alive or dead), but also animals having received organ support for several days (Fig. 1).
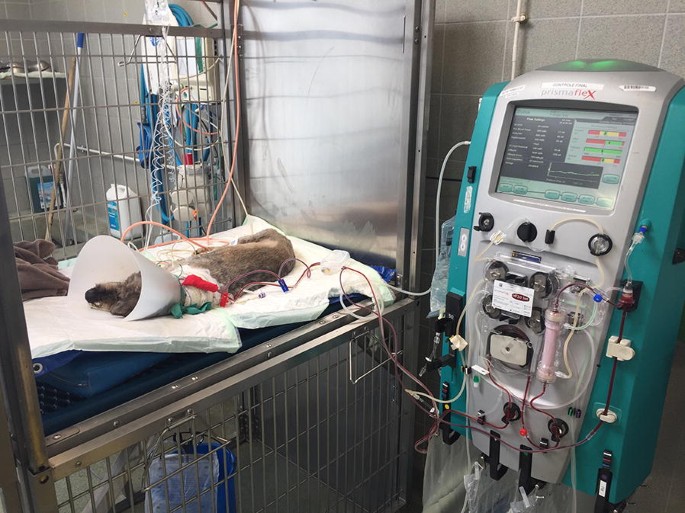
Example of a dog treated for multiple organ failure secondary to leptospirosis infection in the veterinary intensive care unit
Full size image
Another point is that this partnership allows not only to do translational research from animal to human, but also to implement methods used in human medicine to the veterinary ICU; for instance, recently, we introduced the use of high-flow nasal cannula in the veterinary ICU to treat respiratory failure due to viral or bacterial infections in dogs and cats (Fig. 2).

Example of a dog treated with high-flow nasal cannula because of septic respiratory failure
Full size image
In conclusion, animal ICU is probably the next step for research but we believe also that the future is the pooling of veterinary and medical expertise to perform research that will benefit both humans and animals in the ICU which is the "one health" concept.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
References
- 1.
Guillon A, Preau S, Aboab J, Azabou E, Jung B, Silva S, et al. Preclinical septic shock research: why we need an animal ICU. Ann Intensive Care. 2019;9:66.
Article Google Scholar
- 2.
Vassal O, Bonnet J-M, Barthelemy A, Allaouchiche B, Goy-thollot I, Louzier V, et al. Renal effects of amino acids. Acta Anaesth Scand. 2015;59:598–608.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 3.
Pouzot-Nevoret C, Magnin M, Ayoub J-Y, Bourguignon L, Maire P, Wertz D, et al. Evaluation of haemodialysis as a protective technique for preventing high daily dose amikacin nephrotoxicity: an experimental study in an ovine model. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2017;50:148–54.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 4.
Cambournac M, Goy-Thollot I, Guillaumin J, Ayoub J-Y, Pouzot-Nevoret C, Barthélemy A, et al. Acute kidney injury management using intermittent low efficiency haemodiafiltration in a critical care unit: 39 dogs (2012–2015). Acta Vet Scand. 2019;61:17.
Article Google Scholar
- 5.
Barthélemy A, Magnin M, Pouzot-Nevoret C, Bonnet-Garin J-M, Hugonnard M, Goy-Thollot I. Hemorrhagic, hemostatic, and thromboelastometric disorders in 35 dogs with a clinical diagnosis of leptospirosis: a prospective study. J Vet Intern Med. 2017;31:69–80.
Article Google Scholar
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank Philip Robinson (DRCI, Hospices Civils de Lyon) for revision of the manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and Permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baudin, F., Pouzot-Nevoret, C., Louzier, V. et al. Animal ICU… Why not also use the existing veterinary ICUs?. Ann. Intensive Care 9, 93 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13613-019-0568-x
Download citation
-
Received:
-
Accepted:
-
Published:
-
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13613-019-0568-x
Lyon Animal Intensive Care Unit
Source: https://annalsofintensivecare.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s13613-019-0568-x
0 Response to "Lyon Animal Intensive Care Unit"
Post a Comment